Introduction to Soccer Player Diet and Its Impact on Performance

If you’re a soccer ball lover like me, you know the game demands more than just skill with the ball—it demands peak physical condition, stamina, and quick recovery. That’s where a well-crafted soccer player diet steps in to fuel your passion and performance. Whether you’re an aspiring professional, a weekend warrior, or just a fan striving to improve your game, understanding how nutrition supports soccer training is a game-changer.
Soccer is a high-intensity sport involving repetitive sprints, tactical movement, and rapid decision-making, all of which require a finely tuned energy system and muscular endurance. A soccer player diet is specially designed to provide your body with the right nutrients, at the right time, to maximize your energy, optimize recovery, and improve your overall athletic ability.
In this article, I’m excited to dive deep into five winning soccer player diet tips that cover everything from macronutrients and hydration to meal timing and special dietary approaches tailored for you, the soccer ball lover. By the end, you’ll have a clear, actionable plan to fuel your training and games like a pro.
Understanding Energy Metabolism in Soccer Training
Before we explore diet specifics, it’s important to grasp how the body produces energy during soccer. The sport’s variable intensity requires different metabolic pathways:
- Aerobic metabolism: This system powers longer, moderate-intensity phases by breaking down carbohydrates and fats with oxygen. It’s essential for maintaining endurance throughout a full 90-minute match.
- Anaerobic metabolism: During short bursts of high-intensity sprinting or tackling, your body switches to anaerobic energy production, breaking down muscle glycogen without oxygen. This pathway, however, produces lactate, leading to fatigue if energy systems aren’t efficiently replenished.
In essence, soccer players need diets that support both aerobic endurance and anaerobic power. This translates into a balanced consumption of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, along with adequate hydration for optimal metabolic function.
Macronutrient Requirements for Soccer Players

Soccer players’ diets hinge on getting the right balance of macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Let’s break down how each plays a vital role.
The Importance of Carbohydrates in Soccer Player Nutrition
Carbohydrates are the primary fuel source, especially for high-intensity activity like soccer. They’re stored in muscles and liver as glycogen, which fuels both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism. Without enough carbs, you risk early fatigue and subpar performance.
Best Carbohydrate Sources for Sustained Energy
To keep your glycogen stores topped up, focus on:
- Whole grains: Brown rice, whole-wheat pasta, oats, quinoa
- Starchy vegetables: Sweet potatoes, butternut squash, corn
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans
- Fruits: Bananas, apples, berries, oranges
These options release energy steadily, helping maintain endurance throughout training and matches.
Role of Protein in Muscle Repair and Recovery
Protein is king when it comes to repairing micro-tears in muscle fibers after training or games. It supports recovery and muscle growth, preventing injury and enhancing strength.
Lean Protein Sources Ideal for Soccer Athletes
Quality matters. Choose lean, easily digestible sources such as:
- Skinless chicken breast
- Turkey
- Eggs and egg whites
- Low-fat Greek yogurt
- Fish (salmon, tuna, cod)
- Plant proteins like tofu and tempeh
Aim for about 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily, spread evenly across meals and snacks to maximize synthesis.
Healthy Fats and Their Contribution to Overall Health
Fats get a bad rap sometimes, but they’re indispensable for hormone production, brain function, and sustained energy during lower-intensity phases. Healthy fats also support inflammation control, a critical component of recovery.
Recommended Sources of Healthy Fats for Soccer Players
Incorporate these fat sources:
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, chia seeds)
- Avocados
- Olive oil and flaxseed oil
- Fatty fish rich in omega-3s (salmon, mackerel)
Keep fat intake around 20-35% of daily calories, balancing with carbs and proteins.
Hydration Strategies for Soccer Players During Matches and Training
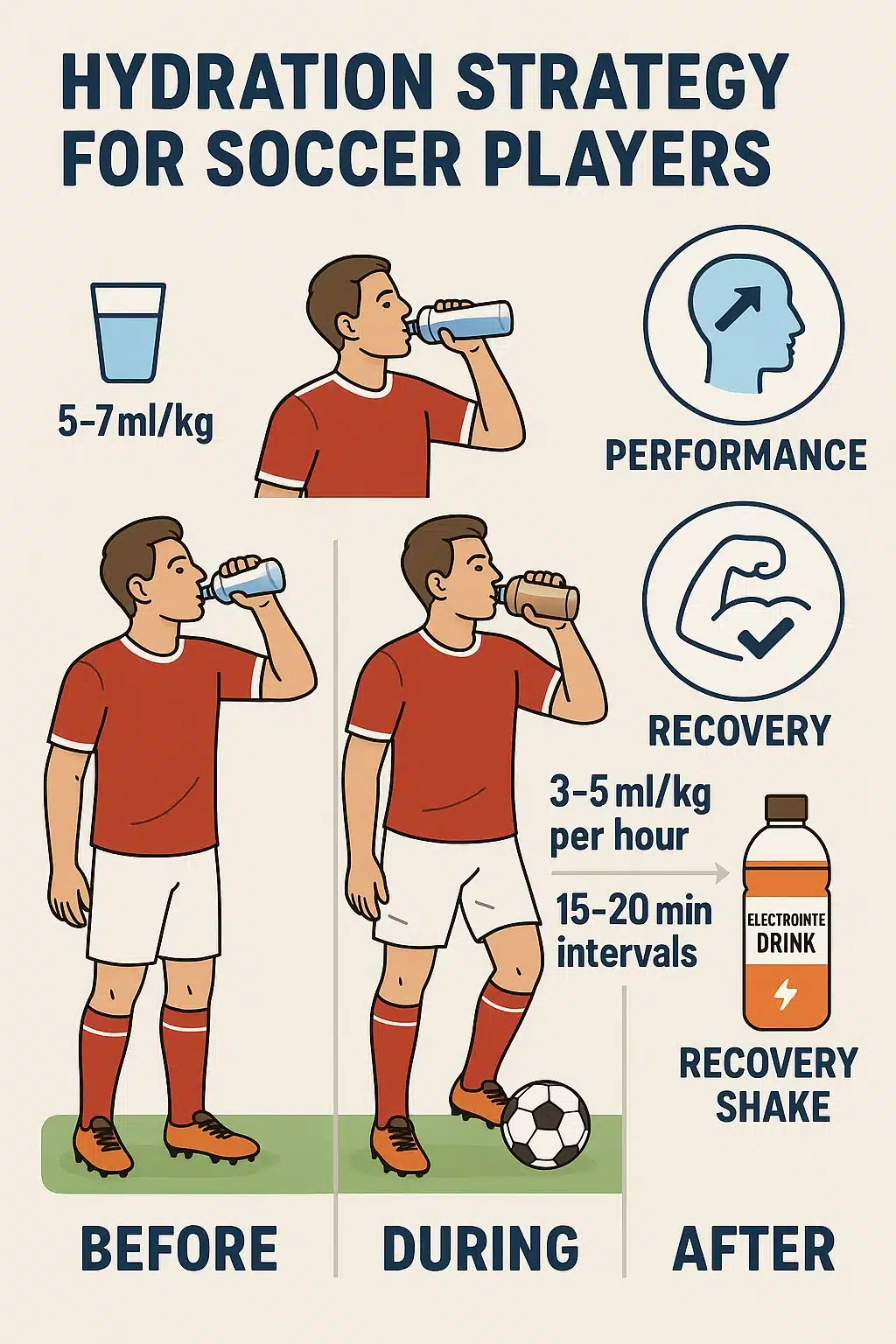
Hydration is often overlooked but is crucial for peak performance and injury prevention. Soccer players can lose 1-2 liters of sweat per hour, risking electrolyte imbalances and heat-related fatigue.
Maintaining Electrolyte Balance for Peak Performance
Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium help regulate nerve impulses and muscle contractions. Sweating depletes these minerals quickly, so replenishment is key.
- Include electrolyte-rich drinks during and after matches. Look for beverages with around 200-300 mg of sodium and potassium per liter.
- Snack on potassium-rich foods like bananas and oranges before or after games.
Timing and Types of Fluids: Water vs. Sports Drinks
- Before exercise: Hydrate with 500-600 ml of water about two hours before kickoff.
- During exercise: Sip 150-250 ml every 15-20 minutes. For sessions longer than 60 minutes, opt for sports drinks with electrolytes and carbohydrates.
- After exercise: Focus on rehydration with water plus a recovery drink containing carbs and protein to assist muscle repair.
Meal Timing Tips for Optimal Soccer Performance
When you eat can be just as important as what you eat for soccer players.
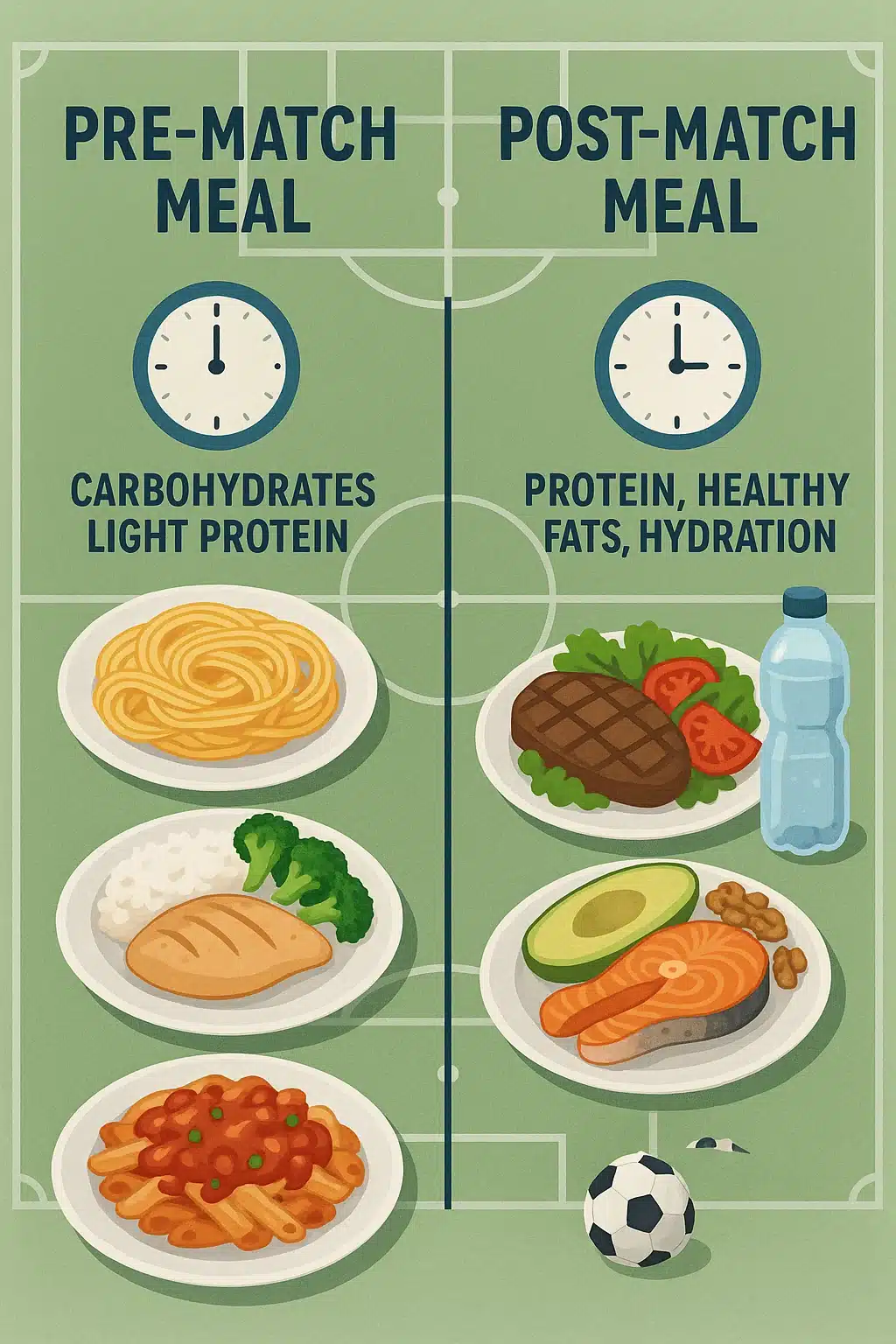
Pre-Game Meal Ideas to Maximize Energy Availability
Eating 3-4 hours before a match or training session gives your body time to digest and store maximum glycogen.
Try meals like:
- Grilled chicken breast with quinoa and steamed broccoli
- Whole-wheat pasta tossed with olive oil, spinach, and turkey meatballs
- Sweet potato mash with steamed green beans and baked salmon
Avoid high-fat or overly fibrous foods pre-game to prevent discomfort.
Post-Training Recovery Foods to Enhance Glycogen Replenishment and Muscle Repair
Within 30-60 minutes after exertion, focus on foods rich in carbs and protein to accelerate recovery and replenish glycogen.
Examples:
- Chocolate milk (a perfect carb-to-protein ratio)
- Greek yogurt topped with mixed berries and a drizzle of honey
- Turkey and avocado sandwich on whole-grain bread
- Smoothie with whey protein, banana, spinach, and almond milk
This timing jumpstarts muscle repair and helps you bounce back stronger for your next match.
Special Dietary Approaches Tailored for Soccer Players
Every player is unique, and some might benefit from specific dietary approaches addressing individual needs or digestive sensitivities.
Overview of the Vertical Diet and Its Benefits
The Vertical Diet focuses on nutrient-dense, easily digestible foods emphasizing red meat, white rice, and select vegetables. Many athletes appreciate its simplicity and powerful effect on digestion and energy. It supports muscle gain and reduces bloating, ideal for high-performance soccer players needing lean mass and quick recovery.
Nightshade-Free Diet for Players with Digestive Sensitivities
Nightshades like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants can aggravate digestive issues for some. This diet removes these foods to reduce inflammation and improve gut health, which can enhance overall athletic performance for sensitive players.
Incorporating Low-FODMAP Vegetables for Digestive Health
Low-FODMAP veggies—such as carrots, zucchini, spinach, and cucumbers—are less likely to cause bloating or gas. Soccer players with IBS or other gut sensitivities may find this approach helpful in maintaining digestive comfort while still obtaining essential nutrients.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals for Soccer Players
Micronutrients often fly under the radar but are just as critical as macronutrients.
Iron Absorption and Its Role in Athletic Performance
Iron is vital for oxygen transport in the blood, making it crucial for aerobic stamina. Soccer players, especially females, risk iron deficiency due to high physical demands and potential dietary shortfalls.
- Boost absorption by pairing iron-rich foods like lean beef and spinach with Vitamin C sources (oranges, bell peppers).
- Monitor iron status regularly with your healthcare provider.
Calcium Intake for Bone Strength and Muscle Function
Strong bones prevent fractures; calcium also aids muscle contraction. Soccer players put repetitive strain on bones and muscles, so ensuring adequate calcium through:
- Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt
- Fortified plant milks
- Leafy greens such as kale and collard greens
supports long-term health and performance.
Foods to Avoid for Reducing Inflammation and Enhancing Recovery
Reducing systemic inflammation speeds recovery and decreases injury risk. Soccer players should limit:
- Processed sugars and refined carbohydrates (candies, pastries)
- Fried and greasy foods
- Excessive red and processed meats
- Artificial additives and preservatives
Instead, embrace anti-inflammatory foods such as turmeric, ginger, berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish rich in omega-3s.
Soccer Nutrition Tips to Boost Endurance and Stamina
Want to outlast your opponents? Focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide long-lasting energy.
Strategic Use of Nutrient-Dense Foods for Long-Lasting Energy
Incorporate whole-food carbs with fiber and protein—like oatmeal with nuts and fruit—to sustain blood sugar levels and prevent crashes. Complex carbs paired with healthy fats and proteins stabilize energy for those crucial final minutes on the field.
Role of Sports Supplements in Performance Support
Certain supplements, when used correctly, can enhance performance:
- Creatine: Supports short bursts of power
- Beta-alanine: May improve muscular endurance
- Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs): Aid recovery and reduce muscle soreness
Remember, supplements should complement—not replace—a balanced diet.
Unique Insight: Integrating Personalized Nutritional Timing Based on Match Schedules and Recovery Cycles
One size doesn’t fit all. Advanced players can tailor their nutrition by using wearable tech and metabolic testing.
Using Wearable Technology and Metabolic Testing to Optimize Diet
Devices like GPS trackers and heart rate monitors provide data on exertion and recovery. Pairing this info with metabolic tests helps calculate individualized calorie and macronutrient needs, ensuring you’re always one step ahead in managing energy stores and recovery phases.
Conclusion: Building a Sustainable Soccer Player Diet for Peak Performance and Longevity
There you have it, soccer ball lovers—a comprehensive inside look at building a winning soccer player diet that fuels your passion and performance. Nutrition isn’t just about what you eat but when and how you eat it, combined with smart hydration and a few personalized tweaks to meet your body’s unique needs.
By balancing carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats; timing your meals strategically; staying hydrated; paying attention to vitamins and minerals; and avoiding foods that ramp up inflammation, you lay a strong foundation for endurance, speed, and quick recovery. Take advantage of the special diet approaches and technologies to elevate your game even further.
Remember, every player’s journey is unique—a sustainable diet is one you can stick with long term without sacrifice. Start putting these soccer player diet tips into practice today, and watch your game transform from the inside out.
FAQs
1. What is the best diet for soccer players to enhance performance?
The best diet includes a balanced intake of carbohydrates for energy, protein for muscle repair, and healthy fats for overall well-being, alongside adequate hydration and micronutrients like iron and calcium.
2. Which pre-game meal ideas work best for soccer players?
Meals combining lean proteins, whole grains, and vegetables eaten 3-4 hours before the game are ideal. For example, grilled chicken with quinoa and steamed broccoli or whole-wheat pasta with turkey meatballs.
3. How important is hydration during soccer matches?
Hydration is vital. Players should drink water before, during, and after matches, supplementing with electrolyte-rich sports drinks during prolonged or intense sessions to maintain balance and prevent fatigue.
4. Can a nightshade-free diet benefit soccer players?
Yes, soccer players with digestive sensitivities to nightshades may find reduced inflammation and better gut comfort by avoiding foods like tomatoes and peppers.
5. What supplements aid soccer performance and recovery?
Supplements like creatine, beta-alanine, and branched-chain amino acids can support short-term power, endurance, and muscle recovery when combined with a solid diet.
Quick Takeaways/Key Points
- Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for soccer players; choose whole grains and fruits for sustained fuel.
- Protein supports muscle repair; include lean meats, dairy, and plant proteins regularly.
- Healthy fats are crucial for hormone health and inflammation control; nuts, oils, and fatty fish are key sources.
- Proper hydration with water and electrolyte drinks prevents fatigue and muscle cramps.
- Strategic meal timing—pre-game and post-training nutrition—maximizes energy use and recovery.
- Special diets like the Vertical Diet and low-FODMAP options cater to individual digestive needs.
- Essential micronutrients like iron and calcium support oxygen transport and bone strength, critical for endurance.
Fuel your love for the beautiful game with nutrition that works as hard as you do on the field!


