Soccer is a beautiful game, and its magic is often shaped by the roles players take on the field. Whether you’re a seasoned fan or someone just falling in love with the sport, understanding soccer positions explained is a game-changer. It’s not just about running after the ball; it’s about where and how players position themselves to influence the match, create chances, and defend like warriors. In this detailed guide, I’ll take you through the six essential soccer positions every enthusiast should know. We’re diving deep into goalkeepers, defenders, midfielders, and forwards—the core building blocks of any team’s style and success. Along the way, we’ll unpack formations, role responsibilities, tactical nuances, and even developmental tips for young players eager to find their soccer identity.
Soccer positions explained in this article aim to give you a solid grasp of how each spot fits into the bigger puzzle. So, grab your mental cleats, and let’s lace up as we unveil the intricacies of these roles and how they shape the electrifying action on the pitch!
Introduction to Soccer Positions and Their Importance
In soccer, every player’s position comes loaded with distinct responsibilities that contribute to the overall team dynamic and match strategy. Understanding these positions is crucial because it not only enhances the way you watch the game but also deepens your appreciation for the tactical battles happening during every kick and pass.
From the goalkeeper who guards the net to the forwards angling for that perfect shot, each role requires specialized skills, awareness, and decision-making. When you know the “soccer positions explained,” you start to see patterns—how defenders block attacks, how midfielders control the tempo, and how forwards exploit openings.
Recognizing these positions also clarifies why certain formations work and how adjusting player roles can shift a team’s fortunes. This knowledge bridges the gap between casual enjoyment and true fandom, empowering you to talk tactics confidently whether you’re watching a local game or the international stage.
Understanding Soccer Formations and Field Layout
Before diving into individual positions, it’s essential to understand how these roles fit within soccer formations and the field layout. Soccer fields are divided into thirds—defensive, midfield, and attacking zones—with formations dictating how many players occupy each area.
Formations like 4-4-2, 4-3-3, or 3-5-2 rearrange player distribution, impacting how positions function. For example, a 4-4-2 includes four defenders, four midfielders, and two forwards, balancing defense and attack. Meanwhile, a 3-5-2 might emphasize midfield control and wing-back attacks.
Soccer positions shift fluidly within these formations. Players need tactical awareness to support teammates and maintain shape, especially when countering opponents’ strategies. The precise positioning within formations influences whether a team presses aggressively or sits back to defend.
The Role of Positioning in Team Dynamics and Strategy
Positioning is the backbone of team dynamics—a well-positioned player can break down an opposing attack or initiate a rapid counterattack. It requires acute spatial awareness, knowing when to hold your position or when to move forward or back.
Coaches emphasize positioning to ensure players cover areas efficiently, limiting vulnerabilities while maximizing attacking options. Good positioning improves passing lanes, intercepts dangerous balls, and creates overloads in certain field zones to outnumber defenders.
Ultimately, soccer positions explained through the lens of positioning offer insight into how teams execute complex strategies seamlessly. It transforms the game from chaos into a choreographed dance where every player understands their place and purpose.
The Goalkeeper: The Last Line of Defense and Tactical Anchor
Without a doubt, the goalkeeper holds one of the most specialized and critical positions in soccer. This player is the last bastion against goals and often the first catalyst for launching attacks.
Key Responsibilities and Goalkeeper Skills
Goalkeepers don’t just stop shots; they organize the defense, distribute the ball, and make split-second decisions that can change a game. Key skills include reflex saves, aerial ability during crosses, positioning to narrow shooting angles, and footwork for establishing passing options.
Modern goalkeepers are expected to participate actively in play by serving as sweepers behind the defensive line, clearing danger with precise long balls, and even starting quick counterattacks. Goalkeepers like Manuel Neuer and Alisson Becker exemplify this “sweeper-keeper” style.
Shot-stopping demands explosive agility while commanding the box requires communication skills to coordinate defenders’ marks during set pieces. Their mindset is unique—they face pressure continuously but must remain calm and composed to inspire confidence in their team.
How Goalkeepers Influence Defensive Tactics and Transition Play
A goalkeeper’s influence extends beyond saves. By reading the game early and distributing wisely, they can control the tempo during transitions—moments that separate great teams from average ones.
For example, a goalkeeper’s long throw or precise kick can bypass midfield pressure, quickly turning defense into attack before opponents organize. This ability forces opposing teams to reconsider aggressive pressing.
Defensively, goalkeepers direct defensive lines and set-up offside traps, playing a vital tactical role. Coaches often build specific defensive systems around their goalkeeper’s strengths and style, highlighting just how pivotal this position really is.
Defensive Positions Explained: From Center-Backs to Wing-Backs
Defense is a multi-layered puzzle, and getting to know the roles within the backline enriches your understanding of the game’s flow.
Differentiating Between Full-Back and Wing-Back Roles
While both full-backs and wing-backs operate on the flanks, their responsibilities differ significantly based on formations and tactics.
Full-backs, typically in a four-defender setup (such as 4-4-2), focus primarily on defense—marking wingers, blocking crosses, and supporting the center-backs. They occasionally join attacks but usually prioritize maintaining defensive solidity.
Wing-backs appear in formations like 3-5-2 where they hold dual roles of defending and providing width in attack. These players cover vast ground, requiring stamina and crossing ability, acting almost like wingers when their team is in possession.
For instance, in teams like Chelsea or Atletico Madrid, wing-backs are crucial in both phases, providing overlaps for forwards and retreating swiftly to thwart counterattacks. This hybrid role demands tremendous versatility and positional awareness.
Defensive Positioning and Its Impact on Team Structure
Center-backs are the defensive backbone, anchoring the defense with strength, aerial prowess, and tactical intelligence. Their positioning often defines a team’s defensive shape—whether holding a compact block or pressing higher up.
Good defenders anticipate threats, communicate with the goalkeeper and midfield, and maintain discipline to avoid unnecessary fouls or gaps. Precise positioning prevents strikers from finding space, forcing errors.
The cohesion among defensive line players is vital. A misstep or poor positioning can unravel an entire defensive unit, making it essential that defensive roles meld into a synchronized system, adapting dynamically to attacking threats.
Numbering System Traditionally Associated with Defensive Roles
Historical numbering in soccer neatly corresponds to positions, helping fans and players alike identify roles instantly.
Defenders usually wear numbers 2 through 5:
– 2: Right full-back
– 3: Left full-back
– 4 and 5: Center-backs
Although modern tactics have blurred these lines, these numbers still anchor soccer’s positional lexicon. Knowing this system helps fans decode match lineups and player duties intuitively.
Midfielders: The Tactical Engines of the Team
If defenders are the fortress and forwards the spear, midfielders are the engine room making the whole system tick. Their influence over possession, tempo, and tactical balance cannot be overstated.
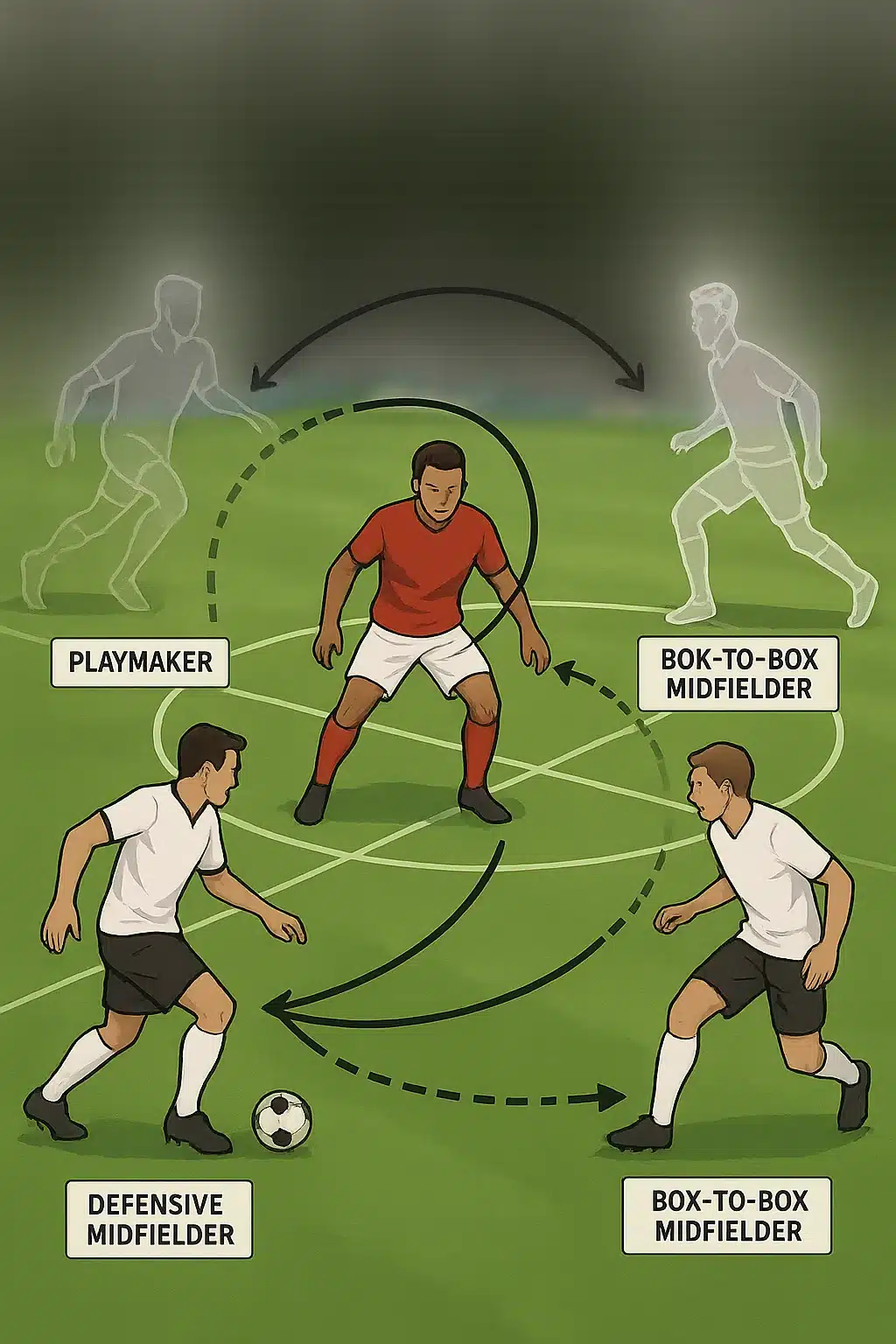
Breakdown of Defensive, Central, and Attacking Midfield Positions
Midfield roles come in varied flavors:
-
Defensive Midfielder (CDM): Acts as a shield for defenders, intercepting passes, breaking up play, and distributing the ball to transition from defense to attack. Think Sergio Busquets — disciplined and strategic.
-
Central Midfielder (CM): The all-rounder who balances defense and offense, dictates tempo, and connects lines. Players like Luka Modrić master this role with vision and work rate.
-
Attacking Midfielder (CAM): Positioned closer to the forwards, often orchestrating attacks with key passes, dribbles, and shots on goal. Known as the “number 10,” legends like Kevin De Bruyne exemplify creativity and flair here.
Each type requires different skill sets but all thrive on spatial awareness, stamina, and passing accuracy.
Midfield Control and Its Influence on Possession and Transition Play
Midfielders control the match rhythm, often dictating possession streaks that wear down opposing teams. Their ability to keep composure under pressure while distributing effectively can open lethal attacking moves.
When transitioning, midfielders decide whether to slow the game down or rapidly exploit defensive lapses, adjusting to the situation instantly. This tactical flexibility keeps games unpredictable and exciting.
Control in midfield also aids in defensive recovery, as midfielders drop back to assist defenders when possession is lost, preventing counterattacks and regaining ball control.
How Midfielders Bridge Defense and Attack with Tactical Flexibility
One of the midfield’s key traits is its bridging role—it connects defense and attack seamlessly. Good midfielders know when to fall back and support defense or when to surge forward to assist forwards.
Because of this, coaches rely heavily on midfielders for tactical switches—like pressing high up to win the ball or retreating to form a compact defensive block.
A flexible midfield allows formations to shift fluidly during games (for example, morphing from 4-3-3 to 4-5-1), granting teams a strategic edge. Understanding these positional nuances enriches how we view midfield battles during matches.
Forwards Explained: Strikers, Wingers, and Their Roles in Goal-Scoring
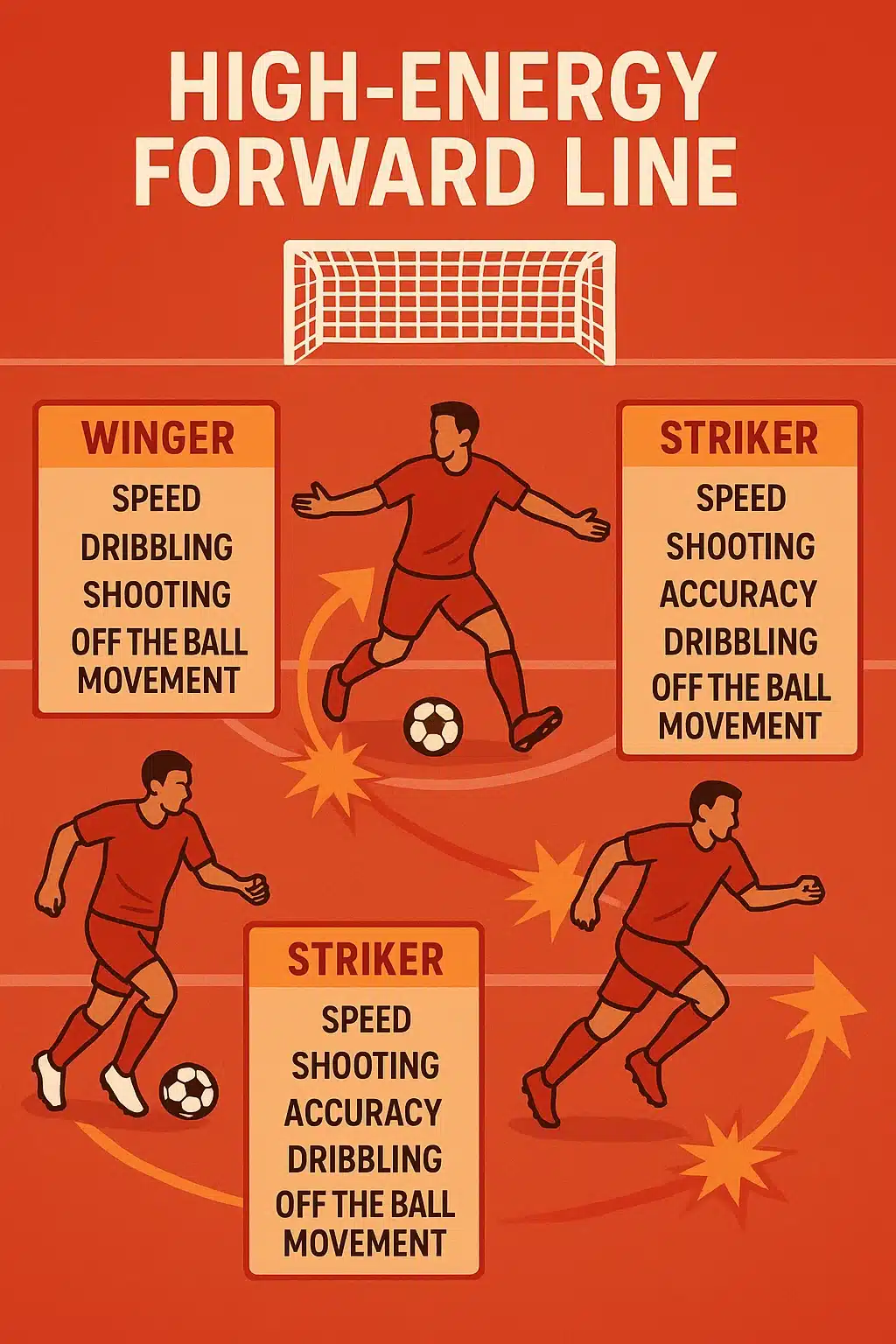
The players tasked with the thrilling job of putting the ball in the back of the net are forward positions. But forwards come with varied responsibilities and playing styles.
Different Forward Roles and Their Responsibilities
-
Striker (Center Forward): The main goal-scorer, typically stationed centrally near the opponent’s goal. Strikers like Robert Lewandowski use strength, positioning, and finishing skills to convert chances.
-
Wingers: Positioned wide, wingers create chances with pace, dribbling, and crosses. They stretch defenses and offer creative outlets from the flanks. Players such as Raheem Sterling excel in this role.
-
Second Striker / False Nine: A more fluid forward who drops deeper to link play, create space, and confuse defenders. Lionel Messi revolutionized this role by blending scoring with playmaking.
Each forward role shapes attacking strategies differently, influencing how teams penetrate defenses and finish chances.
How Forward Positioning Affects Attacking Strategies and Creating Chances
Forward positioning strategically manipulates defensive lines. For example, a striker making runs behind defenders forces the backline to drop deeper, creating space for midfielders to exploit.
Wingers widen the pitch, dragging defenders into wide areas to open central spaces. This stretching tactic allows forwards and attacking midfielders more room to operate.
Smart forwards adjust their positioning based on team tactics—sometimes holding up play, other times darting into pockets of space—making their role essential in orchestrating goal-scoring opportunities.
Traditional vs. Modern Soccer Formations and Their Influence on Positions
Soccer has evolved dramatically, and so have the formations and the roles within those frameworks.
Historical Context of Player Numbering and Position Naming
Originally, formations like the 2-3-5 heavily emphasized attack, with positions defined rigidly by numbers. Number 9 became synonymous with the central striker, while the full-backs held numbers 2 and 3.
Over time, defensive tactics improved, and formations shifted to prioritize balance. The advent of the “WM” formation and subsequent tactics introduced new roles and numbering variations.
Despite modern complexities, numbering remains a cultural touchstone, helping fans and players connect with the game’s rich history.
Popular Formations Used to Explain Position Roles Effectively
Some classic formations that helped clarify soccer positions include:
-
4-4-2: Balanced with two banks of four plus two forwards, it’s perfect for beginners to understand defensive and attacking roles.
-
4-3-3: Offers midfield control and wing dominance, highlighting wing-back and winger dynamics clearly.
-
3-5-2: Showcases wing-backs’ importance and defensive midfielders’ role in connecting defense to attack.
Teaching youth players and fans with these formations simplifies grasping each position’s responsibilities and tactical purpose.
Youth Soccer Positions and Development: Encouraging Versatility Through Role Understanding
Developing young players with knowledge of soccer positions explained is vital to nurture versatile, intelligent athletes.
Importance of Positioning Over Fixed Roles for Young Players
In youth soccer, insisting on strict positional roles too early can limit growth. Instead, exposing players to multiple positions develops adaptability and game understanding.
For example, a young midfielder learning to play as a defender gains insight into defensive responsibilities and positioning, improving overall soccer IQ. Similarly, defenders trying attacking roles develop better ball control and creativity.
Teaching positional awareness rather than fixed roles encourages well-rounded players who can adjust as per match demands.
Training Tips to Develop a Comprehensive Understanding of Soccer Positions
Coaches and parents can foster positional understanding through:
-
Small-sided games: Encourage movement and role rotation, promoting decision-making.
-
Tactical walkthroughs: Use video analysis explaining player roles and positioning.
-
Position-specific drills: Develop skills tailored to each position but integrate game contexts.
-
Encourage communication: Positioning relies on teamwork, so verbal cues boost awareness.
These practical steps help young players internalize the responsibilities attached to soccer positions explained, paving pathways to advanced skill and tactical acumen.
How Soccer Positions Affect Overall Team Tactics and Match Outcomes
Positions form the foundation upon which team tactics and match results are built.
Positioning’s Role in Defensive and Attacking Set Pieces
On set pieces like corners or free kicks, positioning can decide games. Defenders mark attackers tightly, midfielders organize walls, and goalkeepers command the penalty area.
Offensively, forwards position themselves to capitalize on second balls or make runs to exploit the goalkeeper. These choreographed movements highlight the importance of each position knowing their duties perfectly.
Even a slight mispositioning can lead to defensive vulnerabilities or missed scoring chances, emphasizing the critical role of positioning in these high-pressure moments.
Adapting Positions for Tactical Flexibility During Matches
Successful teams shift formations mid-game by moving players into different positions. A defender may step into midfield during attacks; forwards might drop deeper to assist buildup.
Flexibility in positioning allows teams to respond to opponents’ tactics dynamically, maintaining control and exploiting weaknesses.
Understanding this fluidity is crucial for fans aiming to grasp the deeper tactical chess match unfolding beyond raw physical play.
Unique Insight: The Psychological Impact of Positioning on Player Confidence and Team Cohesion
Soccer positions aren’t just physical—they carry a psychological dimension that impacts performance and team unity.
How Understanding Your Role Enhances Individual Performance
When players clearly understand their positional duties, they feel empowered and confident. Knowing when to hold, press, or support teammates reduces hesitation and mistakes.
Confidence in one’s role encourages risk-taking within tactical boundaries, leading to more creativity and effective play.
Positional Awareness as a Factor in Building Team Trust and Communication
Trust flourishes when teammates anticipate each other’s movements, a product of positional awareness. Each player knowing their role fosters smoother communication, fewer errors, and stronger defense or attack cohesion.
This synergy builds a positive team environment, crucial for sustained success and enjoyment of the game.
Conclusion: Mastering Soccer Positions for Enhanced Enjoyment and Deeper Game Understanding
Now that we’ve journeyed through the key soccer positions explained—from the resolute goalkeeper to dynamic forwards—you’re equipped with a richer appreciation for the sport. Each position is a thread in the fabric of team tactics, strategy, and spirit. As a soccer ball lover, understanding these roles unlocks a new level of enjoyment, empowering you to analyze games with depth and passion.
Whether you’re cheering from the stands, coaching young players, or stepping onto the pitch yourself, grasping these positional nuances transforms your connection with the game. It shows you why certain formations succeed, how player roles evolve, and why soccer is as much about brains as it is about brawn.
So next time you watch a match, recall the roles behind the runs and passes. Notice the repositioning, the quick decisions, the coordinated movements driven by deep understanding of soccer positions explained. Dive into that beautiful game with insight—and watch your love for soccer grow even deeper!
FAQs
1. What are the main responsibilities of the goalkeeper in soccer?
The goalkeeper primarily prevents goals by making saves, organizing the defense, commanding the penalty area particularly during crosses and set pieces, and initiating attacks through distribution like throws and kicks. Modern goalkeepers also act as sweepers behind the defense.
2. How do wing-backs differ from traditional full-backs in their soccer roles?
Full-backs focus mainly on defensive duties along the flanks, while wing-backs have dual roles—defending and delivering attacking width. Wing-backs require greater stamina and offensive skills to overlap and feed crosses, especially in formations like 3-5-2.
3. Why is midfield control critical in soccer positions explained?
Midfield control influences possession, game tempo, and transition phases. Midfielders link defense and attack, break opposition play, and orchestrate movements, making this position key to dictating outcomes and maintaining tactical balance.
4. How does the traditional soccer numbering system help explain player positions?
Traditional numbers (2-5 for defenders, 6-8 for midfielders, 9-11 for forwards) align with historical position roles, helping fans quickly identify player duties on the field. While modern tactics evolve, these numbers remain cultural markers of soccer positions.
5. What’s the best approach for developing youth players’ understanding of soccer positions?
Encouraging versatility by rotating players through multiple positions, using small-sided games, tactical teaching through video analysis, and position-specific drills enhances players’ soccer IQ. Emphasizing positional awareness over rigid roles nurtures adaptable and intelligent players.
Key Points to Remember
- Soccer positions explained provide vital insight into how teams function tactically and strategically.
- Goalkeepers anchor defense and initiate play while requiring a mix of physical and mental skills.
- Defensive roles vary; wing-backs combine defense and attack, unlike traditional full-backs.
- Midfielders serve as the tactical engine, controlling game flow through varied roles.
- Forwards possess distinct responsibilities—strikers finish, wingers create width, and false nines link play.
- Understanding formations aids comprehension of positioning and tactical flexibility.
- Youth development benefits from teaching positional awareness across multiple roles.
- Positioning impacts set pieces, match outcomes, and overall team cohesion.
- Psychological confidence stems from understanding individual roles clearly.
- Flexibility in positioning during games fosters dynamic tactical adaptations.
If you enjoyed learning about soccer positions explained and want to deepen your passion, keep following games with fresh eyes, analyze lineups, and maybe even try taking on different positions yourself. After all, this knowledge transforms the way you experience every thrilling moment on the pitch!



