Introduction to Soccer Field Positions and Their Importance
If you’re like me—a passionate soccer ball lover—you know that understanding soccer field positions is like unlocking a secret language of the game. Each position on the field plays a crucial role, not just as an isolated spot but as part of a fluid, dynamic system that dictates how the game unfolds. Whether you’re watching a thrilling match or playing pickup soccer with friends, knowing what each role entails can boost your appreciation and even your own gameplay.
In this detailed guide, I’m going to take you through five essential soccer field positions that every true enthusiast should know. We’ll explore each position’s responsibilities, skills, and impact on team strategy. Plus, I’ll dig into how popular formations shape these positions and share nifty facts about jersey numbers tied to roles, all peppered with examples drawn from top professionals.
By the end of this journey, you’ll have a comprehensive grasp of the roles of each soccer field position, how they interlink, and what makes them unique. So let’s lace up and dive into the heart of the pitch!
The Goalkeeper: The Last Line of Defense

Key Skills and Responsibilities of a Goalkeeper
There’s no denying that the goalkeeper holds arguably the most pressure-packed position on the field. Often called the last line of defense, goalkeepers are responsible not only for stopping shots but also for organizing the backline and starting plays from the back. Exceptional reflexes, diving prowess, sharp decision-making, and commanding presence in the penalty area distinguish a top goalkeeper.
Take Manuel Neuer, for example, whose ability to sweep outside the penalty box and act almost as an extra defender revolutionized the role. Goalkeepers need excellent shot-stopping skills but also have to master positioning in set-pieces, communicate constantly, and use their feet confidently nowadays.
How Goalkeeper Positioning Affects Team Defense and Strategy
Positioning is everything for goalkeepers. Standing too far off the line risks being caught out by close-range shots; too far back and long-range shots become harder to reach. Good goalkeepers read the game to position themselves optimally relative to the ball, teammates, and opponents.
This positioning also impacts the team’s defensive shape. A goalkeeper who distributes well triggers quick counter-attacks and minimizes the opposition’s possession. When you understand what goalkeepers do, you begin appreciating how they influence the entire team’s defensive and offensive balance—even if they rarely leave the penalty area.
Defenders: Guardians of the Backline
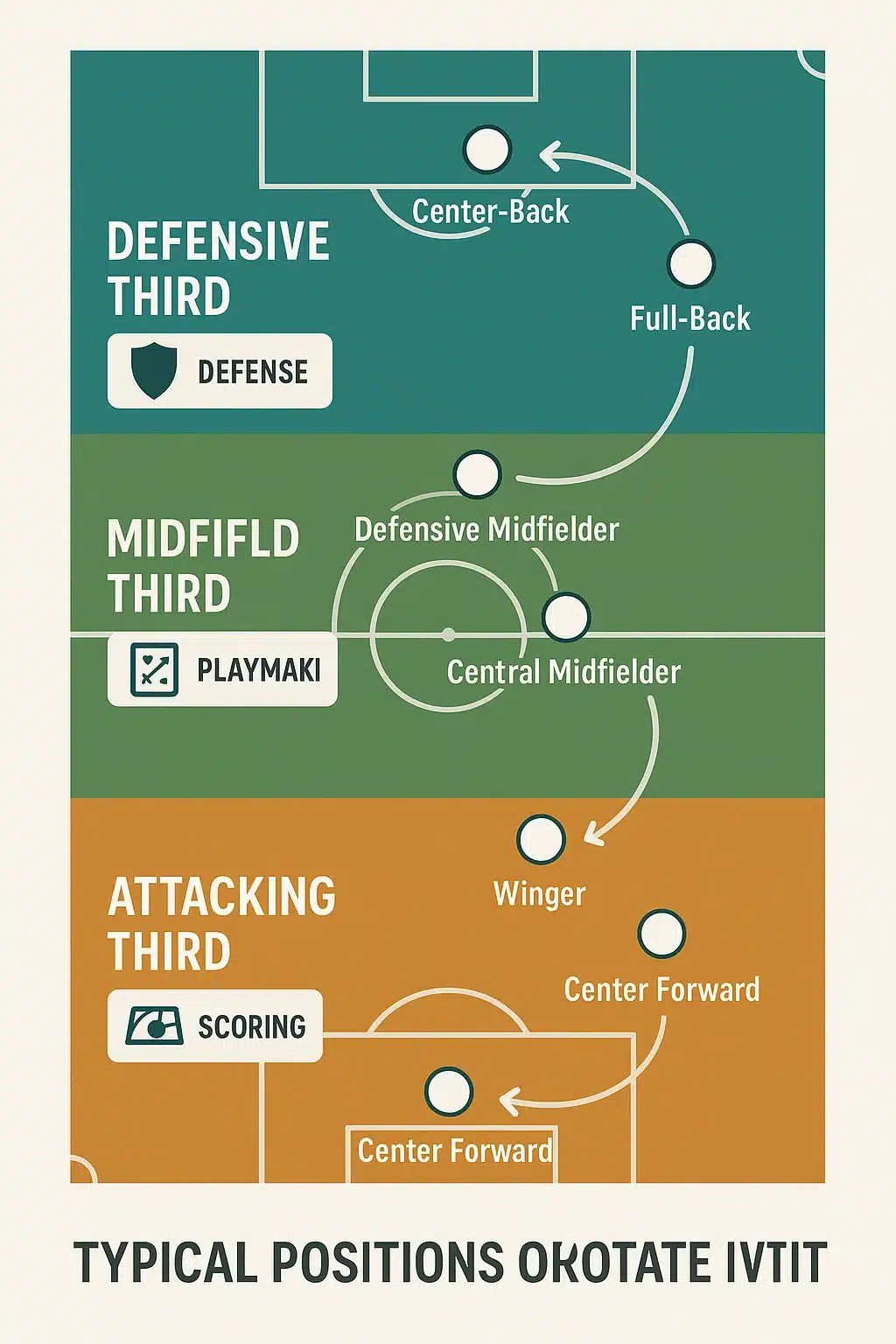
Center Backs: The Heart of Defensive Stability
At the core of any defense are the center backs—the team’s defensive anchors. These players command the center of the defensive third, tasked with blocking attacks, intercepting passes, winning aerial duels, and making crucial tackles.
Tactical Roles and Skills Required for Center Backs
Great center backs read the game like a book. They anticipate attackers’ moves, jockey for position, and time their challenges perfectly. Physical strength, height for headers, composure under pressure, and excellent communication are vital skills.
For instance, Virgil van Dijk is renowned for blending physicality with intelligent positioning. Center backs often organize the defensive line to employ the offside trap and cover for full-backs advancing forward, making teamwork essential here.
Full-Backs vs Wing-Backs: Blending Defense with Attack
In modern soccer, the traditional full-back role has evolved. Full-backs protect the flanks defensively but now often join attacks, delivering crosses or even cutting inside to create chances. Meanwhile, wing-backs take this further—they operate almost as wingers themselves, tasked with covering the entire sideline providing width and pace, particularly in formations like 3-5-2.
Role Comparison and Impact on Modern Formations
While full-backs focus relatively more on defense with incremental attacking support (think Dani Alves or Trent Alexander-Arnold), wing-backs have more offensive freedom and physical demands. They need blazing speed, stamina, and one-on-one skills. The rise of wing-backs has blurred traditional distinctions, adding tactical nuance to defensive and attacking transitions.
The Sweeper Role: A Rare but Strategic Defensive Position
The sweeper (or libero) is a rare but fascinating defensive role. Sweeper’s primary function is to ‘sweep up’ balls that bypass the main defensive line. Positioned behind the center backs, they provide an additional layer of protection and can initiate counter-attacks with forward passes.
Sweeper roles have diminished in today’s zonal marking systems but were pivotal historically, especially in German and Italian teams. Franz Beckenbauer famously embodied this role, blending defensive solidity with unexpected offensive creativity.
Midfielders: The Engine of the Team
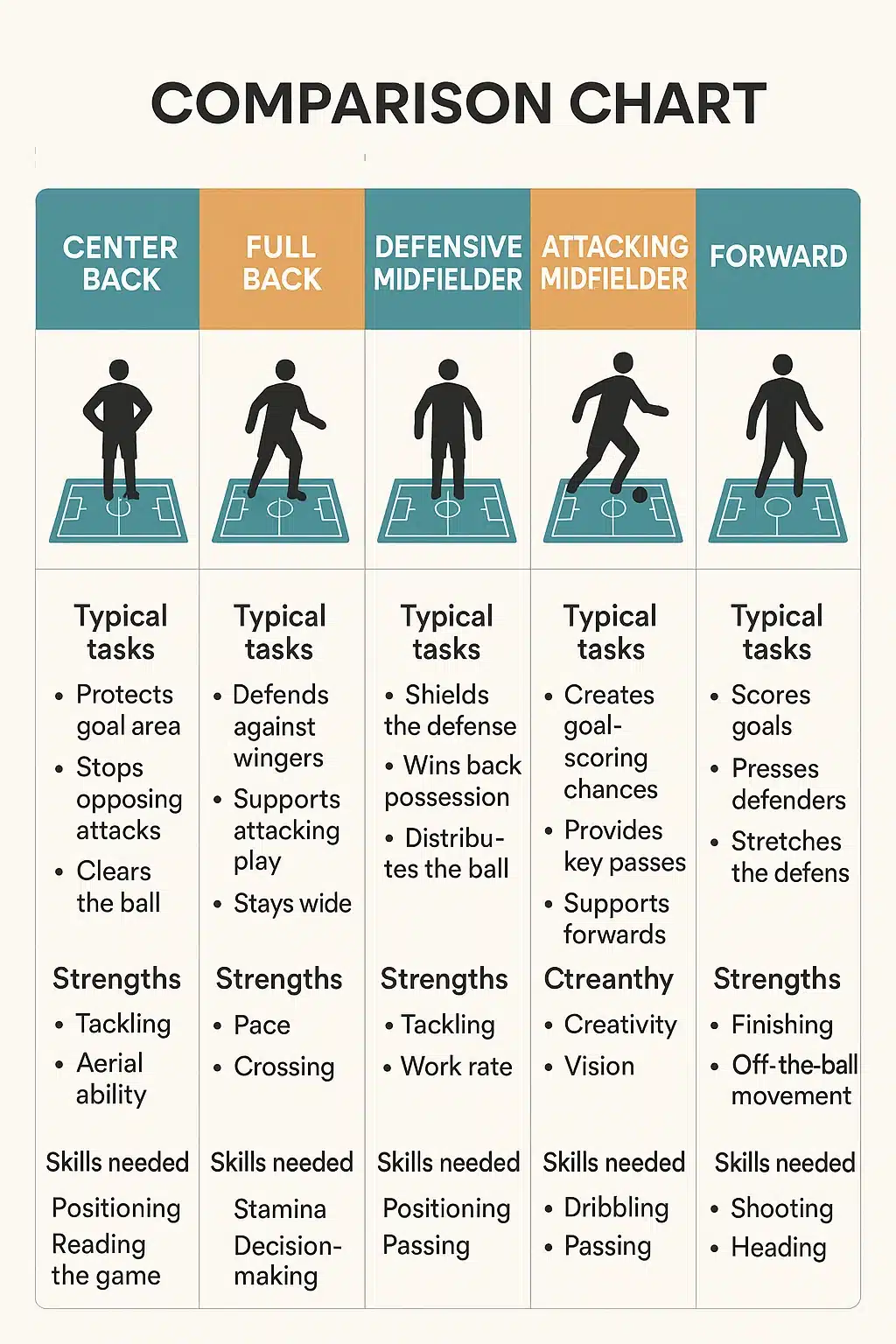
Defensive Midfielders: Shielding the Defense and Initiating Attack
Defensive midfielders act as the team’s protective screen. Positioned in front of defenders, they break up opposition plays, intercept passes, and provide a passing outlet to shift from defense to attack.
Players like N’Golo Kanté excel due to their stamina, tackling precision, and intelligence. The defensive midfielder must balance aggression with tactical discipline, covering gaps and maintaining the team’s shape while simultaneously catalyzing offensive transitions.
Central Midfielders: Controlling the Game’s Tempo
Central midfielders are the game’s metronomes, dictating pace and rhythm. Their responsibilities range from distributing passes, maintaining possession under pressure, to supporting defense and attack. They often act as the pivot, transforming cluttered play into organized build-up.
A prime example is Andrés Iniesta, whose vision and ball control allowed his team to dominate possession and create scoring chances effortlessly. Essential skills here include vision, passing accuracy, endurance, and spatial awareness.
Attacking Midfielders and Second Strikers: Creators of Scoring Chances
Known for flair and creativity, attacking midfielders or number 10s operate just behind the forward line. They unlock defenses with incisive passes, dribbling skills, and shots on goal. Their role sometimes overlaps with second strikers, who combine scoring ability with support play.
Legends like Diego Maradona or Lionel Messi epitomize this role’s dynamism, often changing games singlehandedly. These players need excellent ball control, creativity, and an instinctive feel for goal opportunities.
Wingers: Providing Width and Pace in Attack
Wingers stretch defenses by staying wide and delivering crosses or cutting in to shoot. They blend speed, dribbling, and crossing ability to supply forwards or take shots themselves.
Modern tactics often use inverted wingers—right-footed on the left side and vice versa—to enhance goal-scoring chances. Think Mohamed Salah or Arjen Robben, who regularly cut inside to impressive effect. Wingers must balance attacking zeal with tracking back to support full-backs defensively.
Forwards: The Goal Scorers and Offensive Leaders
Centre-Forward vs Second Striker: Roles and Skills Compared
Center-forwards, or target men, are the focal points of attack. They hold up the ball, battle defenders physically, and score goals. Classic strikers like Robert Lewandowski embody this role, combining strength, aerial ability, and finishing skills.
In contrast, second strikers drift off-center, exploiting spaces, linking play, and scoring opportunistically. They tend to be more agile with creativity, as seen in players like Wayne Rooney during his second striker phase.
Inside Forwards and Modern Variations in Attacking Positions
Inside forwards operate between the winger and striker zones, focusing on cutting inside to shoot or create plays. The fluidity in modern soccer means forwards interchange roles dynamically, confusing defenses.
This evolution means forwards are often versatile, with skills overlapping traditional distinctions, contributing to pressing, build-up, and finishing alike—showcasing the game’s constant development.
How Soccer Formations Influence Player Positions and Roles
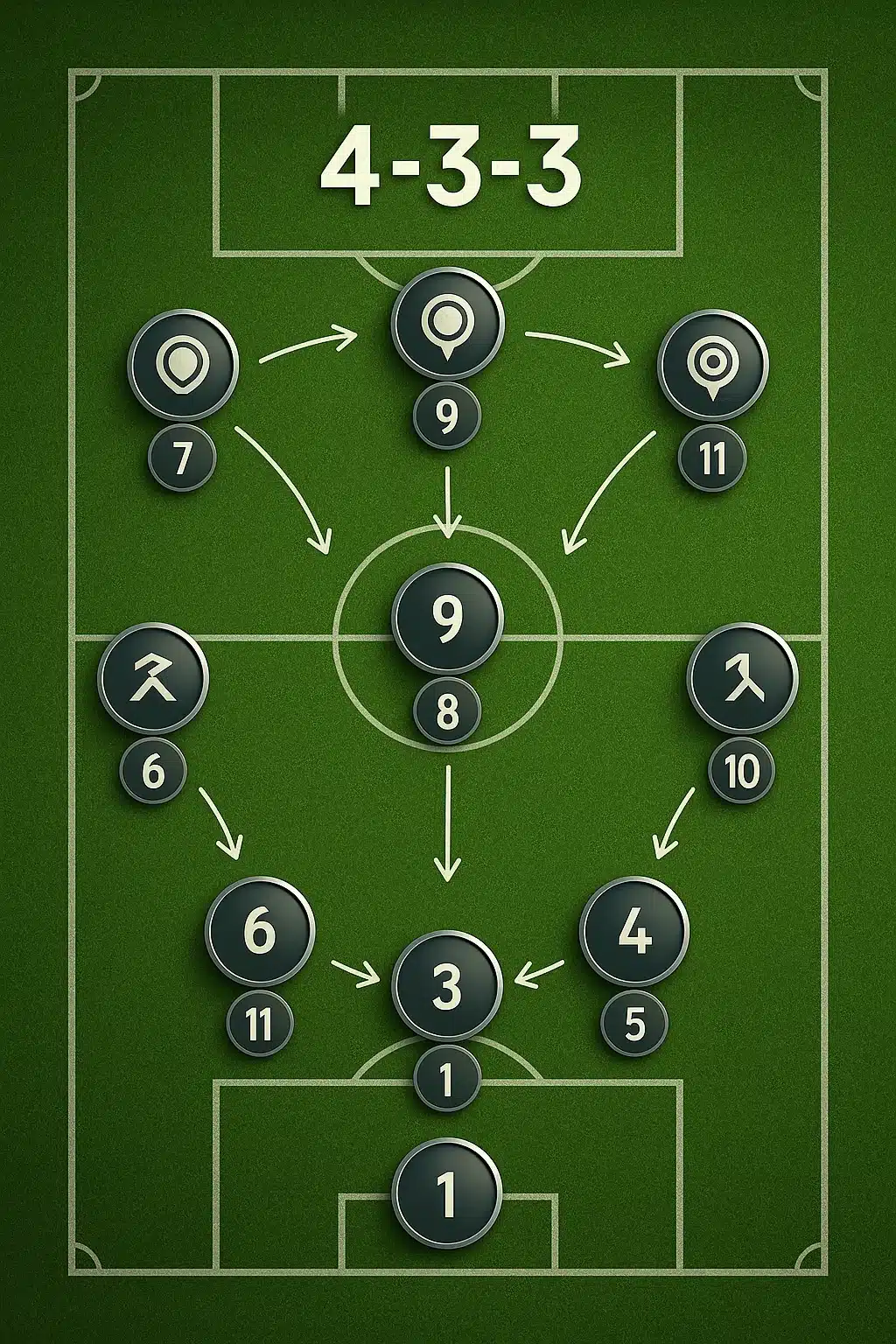
Understanding Common Formations (4-4-2, 4-3-3, 3-5-2) and Their Positioning
Team formations dictate positional alignment and responsibilities. The classic 4-4-2 balances defense and attack with two forwards and a midfield four. The 4-3-3 emphasizes wide attackers and a midfield trio controlling tempo. In 3-5-2, three center backs and wing-backs provide defensive solidity and width.
Each formation tweaks player responsibilities and positioning. For example, wing-backs replace full-backs in 3-5-2, demanding more stamina. Midfielders in a 4-3-3 often divide into defensive anchor, playmaker, and box-to-box roles.
Adapting Positions to Tactical Demands and Opponent Strategies
Coaches adjust positions and formations to counter opponents’ strengths or exploit weaknesses. This dynamic often results in players adopting hybrid roles, such as midfielders dropping deeper or defenders pushing higher.
Understanding these changes can deepen your tactical appreciation as a soccer ball lover, revealing how a single position’s role can vary drastically depending on the game situation.
The Significance of Jersey Numbers and Position Traditions
Historical Numbering Systems and Their Modern Interpretations
Traditionally, jersey numbers corresponded to specific positions: 1 for goalkeeper, 2 and 3 for full-backs, 9 for center-forward, 10 for attacking midfielder. Though modern squads use squad numbering more flexibly, these historic associations persist culturally.
For example, the number 10 jersey often symbolizes the team’s creative heartbeat, while number 9 remains the quintessential goal scorer. Understanding these traditions adds flavor to your knowledge as you watch games unfold.
Famous Professional Players and Their Iconic Positions by Number
Iconic players like Pelé (#10), Cristiano Ronaldo (#7), or Paolo Maldini (#3) are forever linked to their numbers and positions, influencing generations. Their styles help define what these positions demand technically and mentally, enriching your appreciation of soccer field positions.
Position-Specific Skills Every Soccer Enthusiast Should Develop
Essential Techniques for Defenders, Midfielders, and Forwards
Every position requires unique core skills:
– Defenders: tackling, marking, aerial duels, positioning
– Midfielders: passing accuracy, vision, ball control, stamina
– Forwards: shooting, dribbling, off-the-ball runs, composure
By practicing these, you not only improve but deepen your understanding of how different roles operate on the pitch.
Physical and Mental Attributes That Enhance Each Position
Physical attributes (speed, strength, endurance) and mental traits (decision-making, anticipation, composure) are crucial. For example, wingers rely heavily on speed and agility, while center backs depend on strength and concentration.
Soccer is a game of brains as much as brawn—mental toughness often separates good players from great.
Youth Soccer Field Positions and How They Shape Future Talent
Teaching Positional Awareness and Role Responsibilities at Youth Level
Introducing young players to positional concepts early builds tactical awareness. Coaches encourage understanding of spatial roles, movement patterns, and teamwork, laying a foundation for advanced skills.
Developing Versatility and Understanding Through Position Rotation
Rotating children through different positions exposes them to diverse responsibilities, fostering versatility and empathy for teammates’ roles. This approach produces well-rounded players and develops creativity and tactical flexibility.
Unique Perspectives: The Evolution of Hybrid Roles in Soccer Positions
Emergence of Versatile Players Blurring Traditional Position Lines
Modern soccer celebrates players who can seamlessly switch between defense, midfield, and attack, blurring classical lines. Think of Philipp Lahm, a defender turned midfielder, or Lionel Messi dropping deep to orchestrate attacks.
How Modern Tactics Create Dynamic Position Interchanges On the Field
Tactical innovations encourage fluid movement, with forwards defending and defenders attacking—a far cry from the rigid roles of the past. This adaptability makes soccer more exciting and challenging, perfect for enthusiasts eager to dive deep into positional nuances.
Conclusion: Mastering Soccer Positions to Enhance Your Understanding and Enjoyment of the Game
As a true soccer ball lover, mastering the knowledge of soccer field positions transforms how you experience the game. You start seeing the intricate dance of roles, responsibilities, and tactics that create the beautiful game’s drama. Whether you aspire to improve your own playing, coach young talent, or simply become a savvier viewer, understanding these five essential positions—goalkeeper, defender, midfielder, forward, and their key sub-roles—gives you a solid grounding.
Remember, great soccer is not just about flashy skills; it’s about how each player fits into the team framework, adapting fluidly during the match. So next time you sit down with friends or watch a match, keep an eye on how each position contributes uniquely and dynamically. With this knowledge under your belt, your passion for soccer will only deepen, making every match that much more thrilling.
Keep loving the game, learning, and perhaps trying out new positions yourself—you never know where the ball might take you!
FAQs
1. What are the main roles of each soccer field position?
Each soccer position has distinct roles: goalkeepers defend the goal, defenders protect the backline, midfielders control play and link defense and attack, while forwards are responsible for goal scoring and offensive pressure.
2. How do full-backs and wing-backs differ in soccer formations?
Full-backs primarily defend the flanks with occasional offensive support, while wing-backs operate more aggressively along the wings, balancing defense and attack, especially in formations like 3-5-2.
3. What skills should a defensive midfielder focus on developing?
Defensive midfielders benefit from strong tackling, positional awareness, quick passing, and stamina to shield the defense and support attacking transitions efficiently.
4. How do soccer formations influence player positions?
Formations like 4-4-2 or 4-3-3 dictate how many players occupy each part of the field and their roles, shaping how defenders, midfielders, and forwards interact during the game.
5. Why are jersey numbers significant in understanding soccer positions?
Jersey numbers historically corresponded to specific positions, making them symbolic indicators of a player’s traditional role, adding a layer of cultural and tactical meaning to the game.
Quick Takeaways / Key Points
- The goalkeeper is the pivotal last line of defense with specialized skills and position awareness.
- Defenders include center backs, full-backs, wing-backs, and sweepers, each with unique tactical roles.
- Midfielders serve as the engine room—defensive midfielders shield defenses while attacking midfielders create chances.
- Forwards include center-forwards, second strikers, and inside forwards, focusing on scoring and offensive creativity.
- Formations dramatically influence positioning, with roles adapting to team tactics and opponent strategies.
- Jersey numbers hold historical positional significance, enriching the cultural understanding of the game.
- Developing position-specific skills enhances playing level and tactical appreciation.
- Youth positional training fosters tactical understanding and player versatility.
- Modern soccer embraces hybrid roles, increasing tactical dynamism on the field.
- Mastery of soccer field positions deepens your enjoyment, strategy insight, and love for the game.



